Creating Your First Yii Application
To give you an initial experience with Yii, in this section we describe how to
create your first Yii application. We will use yiic (command line tool)
to create a new Yii application and Gii (powerful web based code generator)
to automate code creation for certain tasks. For convenience,
we assume that YiiRoot is the directory where Yii is installed, and WebRoot
is the document root of our Web server.
Run yiic on the command line as follows:
Note: When running
yiicon Mac OS, Linux or Unix, you may need to change the permission of theyiicfile so that it is executable. Alternatively, you may run the tool as follows,
This will create a skeleton Yii application under the directory
WebRoot/testdrive. The application has a directory structure that
is needed by most Yii applications.
Without writing a single line of code, we can test drive our first Yii application by accessing the following URL in a Web browser:
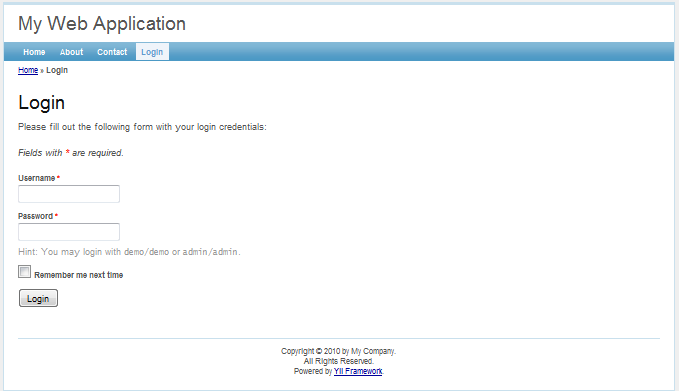
As we can see, the application has four pages: the homepage, the about page, the contact page and the login page. The contact page displays a contact form that users can fill in to submit their inquiries to the webmaster, and the login page allows users to be authenticated before accessing privileged contents. See the following screenshots for more details.
Home page
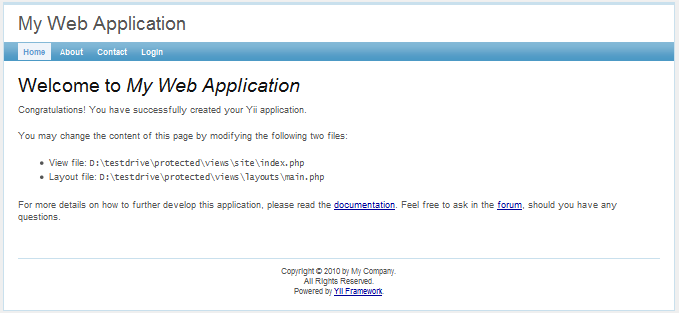
Contact page
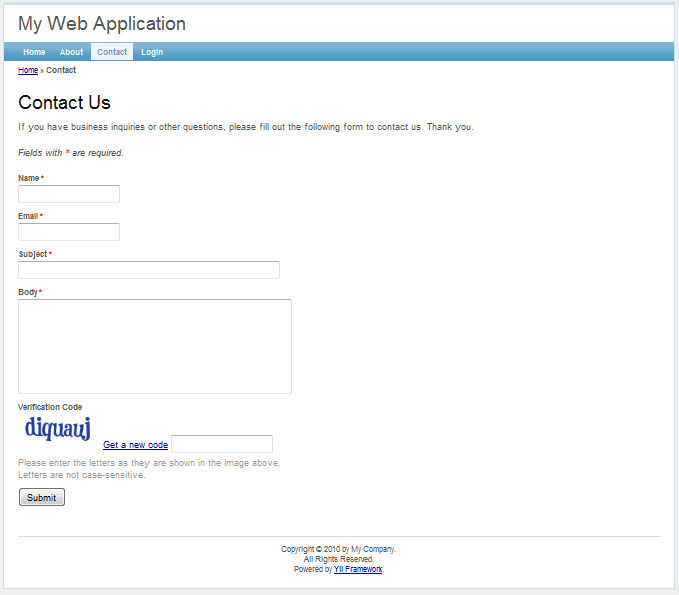
Contact page with input errors
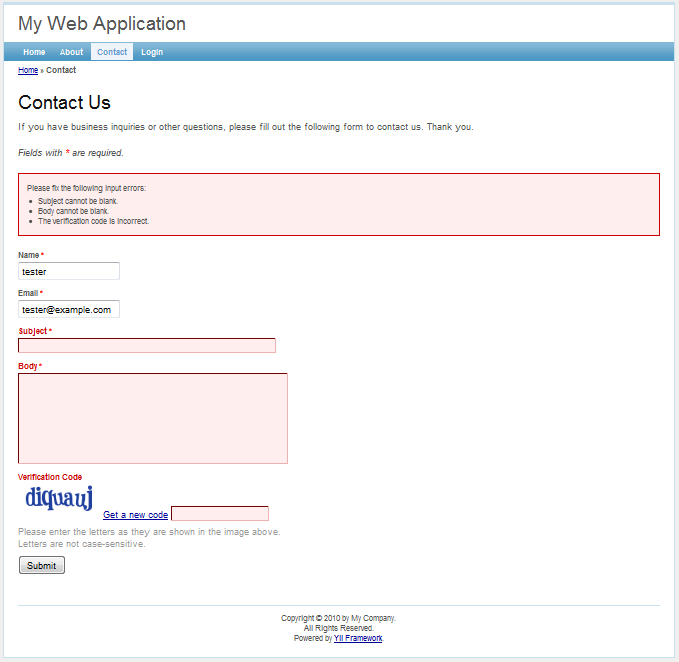
Contact page with success message
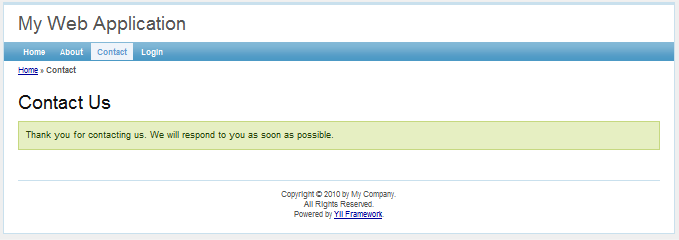
Login page
The following diagram shows the directory structure of our application. Please see Conventions for a detailed explanation.
Application generator described above also supports creation of files needed
by Git version control system. The following command would create necessary
.gitignore (e.g. content of the assets and runtime shouldn't be tracked)
and .gitkeep (forces tracking of initially empty but important directories)
files:
Another supported VCS is Mercurial: pass the hg value as third parameter in
case you're using this VCS. This feature is available since version 1.1.11.
Connecting to Database
Most Web applications are backed by databases. Our test-drive application
is not an exception. To use a database, we need to tell the
application how to connect to it. This is done in the application
configuration file WebRoot/testdrive/protected/config/main.php, highlighted as follows,
The above code instructs Yii that the application should connect to the SQLite database
WebRoot/testdrive/protected/data/testdrive.db when needed. Note that the SQLite database
is already included in the skeleton application that we just generated. The database
contains only a single table named tbl_user:
If you want to try a MySQL database instead, you may use the included MySQL
schema file WebRoot/testdrive/protected/data/schema.mysql.sql to create the database.
Note: To use Yii's database feature, we need to enable the PHP PDO extension and the driver-specific PDO extension. For the test-drive application, we need to turn on both the
php_pdoandphp_pdo_sqliteextensions.
Implementing CRUD Operations
Now comes the fun part. We would like to implement CRUD (create, read,
update and delete) operations for the tbl_user table we just created. This is
also commonly needed in practical applications. Instead of taking the trouble
to write the actual code, we will use Gii -- a powerful Web-based code generator.
Info: Gii has been available since version 1.1.2. Before that, we could use the aforementioned
yiictool to accomplish the same goal. For more details, please refer to Implementing CRUD Operations with yiic shell.
Configuring Gii
In order to use Gii, we first need to edit the file WebRoot/testdrive/protected/config/main.php, which is known as the application configuration file:
Then, visit the URL http://hostname/testdrive/index.php?r=gii. We will be prompted for a password, which should be the one that we just entered in the above application configuration.
Generating the User Model
After login, click on the link Model Generator. This will bring us to the following model generation page,
Model Generator
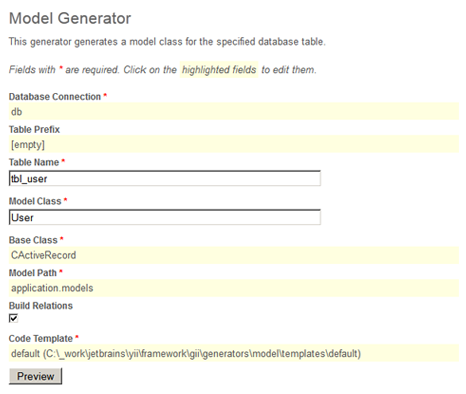
In the Table Name field, enter tbl_user. In the Model Class field, enter User. Then press the Preview button. This will show us the new code file to be generated. Now press the Generate button. A new file named User.php will be generated under protected/models. As we will describe later in this guide, this User model class allows us to talk to the underlying database tbl_user table in an object-oriented fashion.
Generating CRUD Code
After creating the model class file, we will generate the code that implements the CRUD operations about the user data. We choose the Crud Generator in Gii, shown as follows,
CRUD Generator
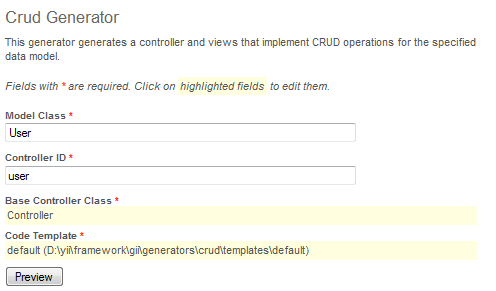
In the Model Class field, enter User. In the Controller ID field, enter user (in lower case). Now press the Preview button followed by the Generate button. We are done with the CRUD code generation.
Accessing CRUD Pages
Let's enjoy our work by browsing the following URL:
This will display a list of user entries in the tbl_user table.
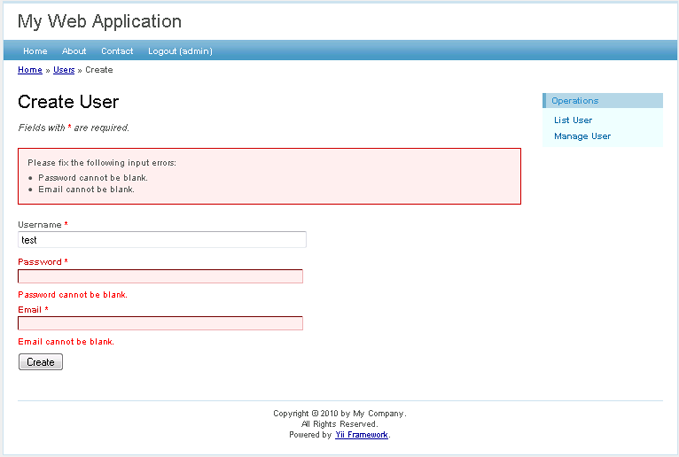
Click the Create User button on the page. We will be brought to the login
page if we have not logged in before. After logging in, we see
an input form that allows us to add a new user entry. Complete the form and
click the Create button. If there is any input error, a nice error
prompt will show up which prevents us from saving the input. Back on the
user list page, we should see the newly added user appearing in the list.
Repeat the above steps to add more users. Notice that the user list page will automatically paginate the user entries if there are too many to be displayed in one page.
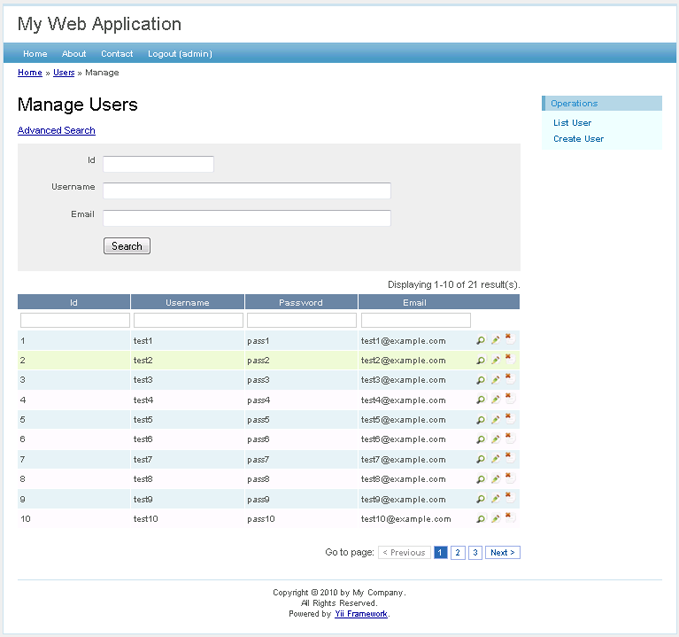
If we login as an administrator using admin/admin, we can view the user
admin page with the following URL:
This will show us the user entries in a nice tabular format. We can click on the table header cells to sort the corresponding columns. We can click on the buttons on each row of data to view, update or delete the corresponding row of data. We can browse different pages. We can also filter and search to look for the data we are interested in.
All these nice features come without requiring us to write a single line of code!
User admin page
Create new user page